Briefing binder for the Minister of Tourism and Minister responsible for CED - 2023
About this publication
Publication author: Canada Economic Development for Quebec Regions
Publish date: November 23, 2023
Table of Contents
- CED: Mandate and Strategic Approach
- Intervention Priorities
- Means of action (Programs and Initiatives)
CED: Mandate and Strategic Approach
Regional development: Canada’s approach
- Regional economic development helps reduce economic disparities among regions and promote balanced, sustainable growth across Canada
- Allows for leveraging of the specific advantages of each region, fostering local job creation and strengthening economic resilience in the face of external shocks
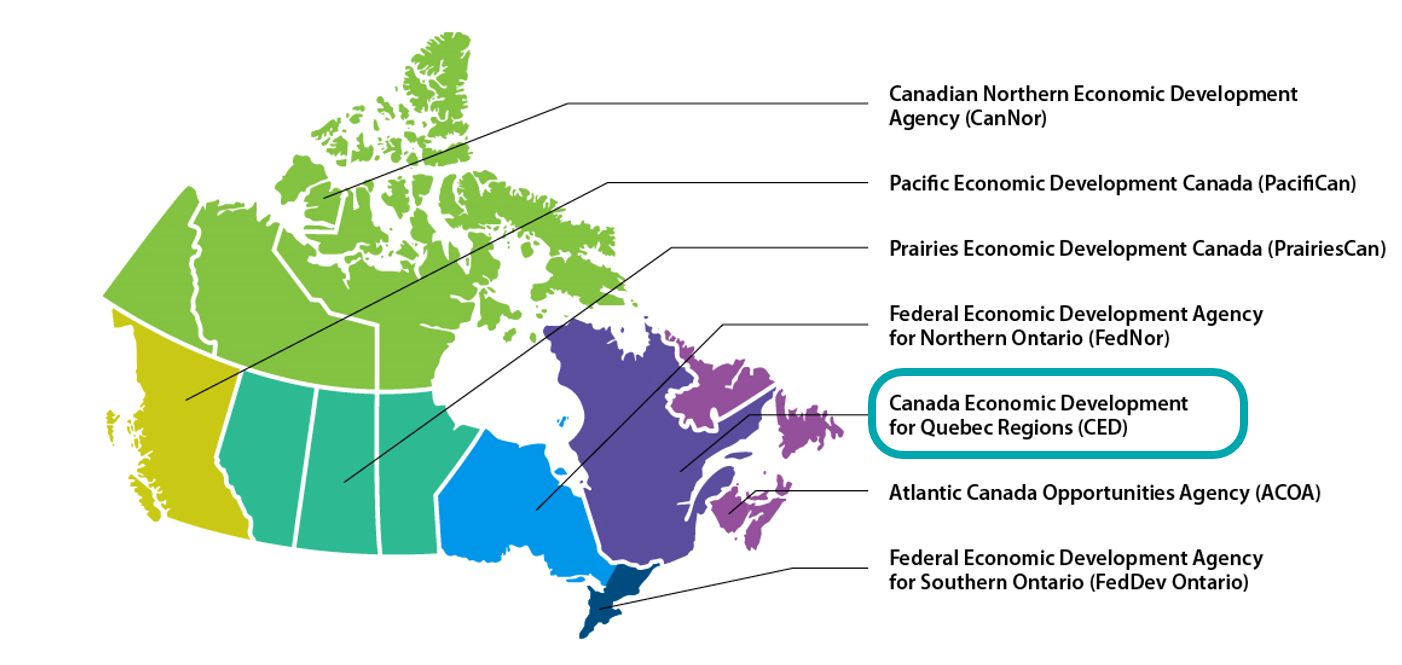
Text version of Regional representation
| Province/Territory | Regional development agency support |
|---|---|
| Nunavut | Canadian Northern Economic Development Agency (CanNor) |
| Yukon | Canadian Northern Economic Development Agency (CanNor) |
| Northwest Territories | Canadian Northern Economic Development Agency (CanNor) |
| British Columbia | Pacific Economic Development Canada (PacifiCan) |
| Saskatchewan | Prairies Economic Development Canada (PrairiesCan) |
| Alberta | Prairies Economic Development Canada (PrairiesCan) |
| Manitoba | Prairies Economic Development Canada (PrairiesCan) |
| Ontario | Northern Ontario: Federal Economic Development Agency for Northern Ontario (FedNor) Southern Ontario: Federal Economic Development Agency for Southern Ontario (FedDev Ontario) |
| Quebec | Canada Economic Development for Quebec Regions (CED) |
| New Brunswick | Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency (ACOA) |
| Newfoundland and Labrador | Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency (ACOA) |
| Nova Scotia | Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency (ACOA) |
| Prince Edward Island | Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency (ACOA) |
The only federal entities with a mandate firmly rooted in regional dynamics
- Deliver programs tailored to all communities in their region, including small and rural communities
- Make up part of a continuum of support for businesses, thus ensuring the coherence and complementarity of interventions by:
- Other federal agents
- Provincial and economic players in the regions
- High added value:
- Create conditions for growth for, and with, the regions
- Build on local assets and players
- Support flexible, regional solutions focused on SMEs and ecosystems
CED: a key federal partner in Quebec’s regional economic development
Mission
“Promote the long-term economic development of the regions of Quebec by giving special attention to those where slow economic growth is prevalent or where opportunities for productive employment are inadequate.
Foster co-operation and complementarity with Quebec and its communities.” - Section 10 of the Act
We support Quebec businesses and the regions of Quebec as they transition to the economy of tomorrow—a greener and more innovative and inclusive economy.
- By focusing our interventions on SMEs, directly or through non-profit economic organizations
- By focusing on innovation and diversification as levers of development
- By prioritizing projects that generate long-term economic benefits
- By doing more than just funding promising projects: CED acts as a facilitator, helping bring together the right partners around a given project
A distinct role within a continuum of federal assistance
| Primary Clientele | Main Types of Projects | Sectors Targeted | Type of Assistance Provided | Amount of Assistance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRC-IRAP | SMEs | R&D Demonstration |
All |
Non-Repayable Advisory Services | Less than $10M | R&D |
| Canada Innovation Corporation |
TBD |
R&D Commercialization | TBD | TBD | TBD | R&D and commercialization |
| SDTC | SMEs | R&D Demonstration Commercialization | Clean Technology | Non-Repayable | Generally $3M Startups $100,000 | Specializing in the dev. of clean tech |
| CED (and the RDAs) | SMEs Ecosystems (NPOs) | Growth (adoption, demonstration, productivity, commercialization, expansion) and support for SMEs; ecosystem structuring | All | Non-Repayable Repayable | Generally less than $3M | Flexible, regional solutions focused on SMEs and ecosystems |
| BDC | SMEs | Varies | All | Commercial Loans Venture Capital Advisory Services | Varies | Commercial bank |
| SIF / Net Zero Accelerator (ISED) | Ecosystems (NPOs/Consortia) Large Businesses | R&D Demonstration Commercialization | All | Non-Repayable Repayable | Over $20M | Major projects |
| Canada Growth Fund | TBD | TBD | Low-Carbon | Various Tools | TBD | Major projects |
| Sector-oriented departments | Varies | Varies | Each with its Own Sector | Non-Repayable and Repayable | Varies | Sector-based approach |
Distinct place-based service offer
National Priorities and Policies
- Fosters reflection at the national level
- Program design and implementation tailored to actual needs on the ground
An economic development approach rooted in the community (place-based)
- Funding Tailored to Needs: Provide financial support and ensure risk-sharing, by delivering regional programs that promote growth through innovation, the green transition, and economic diversification; and national initiatives to address targeted economic issues
- Credible antennae on the ground: Promote the regional lens and provide on-the-ground intelligence regarding pan-Canadian government programs and for interdepartmental collaborative projects
- Coordinated Response: Ensure synergy, networking and complementarity of interventions by co-operating with various partners and levels of government (federal, provincial and municipal; Indigenous communities; economic development agencies; universities; and other community stakeholders)
- Support: Support SMEs in their forward-looking projects at all stages of their development (referrals, networking, etc.)
Intervention logic based on regional realities
Expertise firmly rooted in the regions with 12 business offices across Quebec
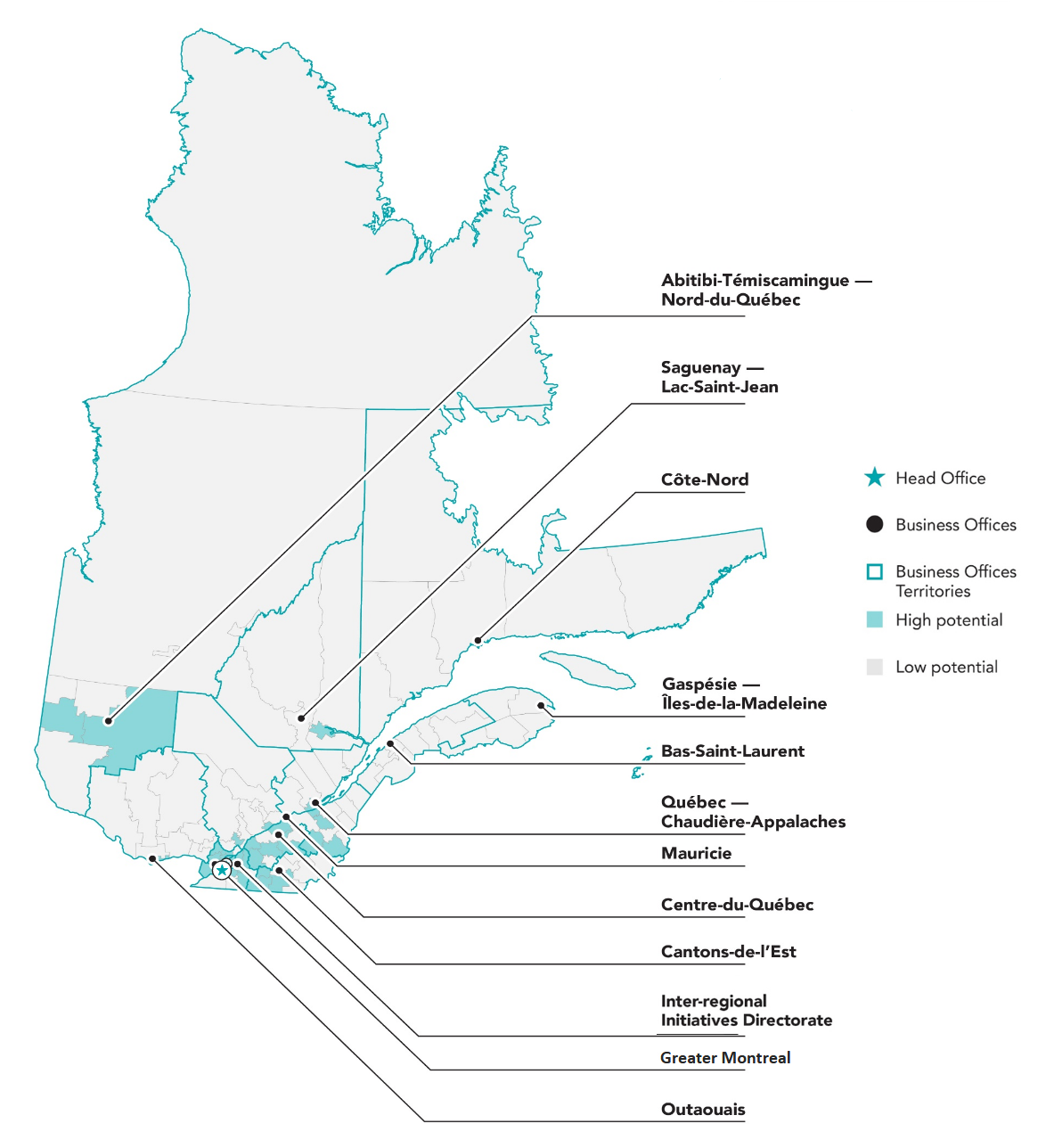
Text version:
Legend:
- Head Office
- Business Office
- Business Offices Territories
- High Potential
- Low Potential
Regions:
- Abitibi Témiscamingue - Nord du Québec
- Saguenay - Lac Saint Jean
- Côte-Nord
- Gaspésie - Îles-de-la-Madeleine
- Bas-St-Laurent
- Québec - Chaudière-Appalaches
- Mauricie
- Centre-du-Québec
- Cantons-de-l’Est
- Inter-regional Initiatives Directorate
- Greater Montreal
- Outaouais
Interventions tailored based on...
...the reality on the ground
- Sub-regional disparities: 75 of the 104 regional county municipalities (RCMs) have lower economic development potential
- Factors that influence development in the various regions: workforce, market access, entrepreneurial pool, single-industry status, demographics, urban and rural areas, resources, Indigenous land, etc.
- The strengths and assets specific to each region and upon which they can rely for their economic development
...the broader institutional setting
- CED seeks complementarity with the actions of the Government of Quebec and players on the ground
- CED benefits from a Quebec government omnibus decree that facilitates the implementation of its programs when dealing with organizations subject to Quebec’s M-30 legislation
An approach that takes Quebec’s specific institutional context into account
A host of key players structure the lives of members of the public and businesses, identify needs, formulate policies and implement interventions
Interventions by CED and the federal government must take into account
- The Act that governs intergovernmental affairs: M-30
- The Government of Quebec, which actively intervenes and uses these key structures and actors
Actors
- Interventionism of provincial government organizations in a number of areas, including digitization, tourism, etc.
- Weight and complexity of the patchwork of support organizations (NPOs) in Quebec
Area
- 17 administrative regions
- 104 RCMs
- 1,131 municipalities
- Nearly 60 Indigenous communities
Education
- Network of CPEs (daycares)
- CEGEPs and Université du Québec network
- CCTTs: college centres for technology transfer
Economy and business
- Investissement Québec
- Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec
- Montréal International
- Québec International
- ORPEX (Exports)
- ATRs-ATSs (Tourism)
- Sector clusters
Energy and the environment
- Hydro-Québec
- Horizontal industrial clusters (ÉcoTech, Propulsion QC)
Intervention Priorities
Interventions aligned with Government of Canada priorities...
Results for Canadians:
- Government of Canada Priorities
- CED’s Departmental Plan
- Implementation Priorities and Budget
- Regional Intervention Strategies
- Projects
That address Quebec’s economic issues
Economic Uncertainty
- Issues
- Impact of inflation on operating costs
- Monetary tightening: downward pressure on economic activity (rising cost of borrowing)
- Intervention Priorities
- Boost the competitiveness and growth of Quebec businesses
- Foster the economic resilience of businesses and the regions (temporary)
Labour Shortage
- Issues
- Aging population
- Significant increase in the number of vacancies since 2017
- Pressure on SMEs (postponement of projects or refusal of contracts; wage increases)
- Intervention Priorities
- Boost the competitiveness and growth of Quebec businesses
- Foster the economic resilience of businesses and the regions (temporary)
Gaps in Commercialization / Global Restructuring
- Issues
- Insufficient linkage between manufacturing and innovation
- Decoupling and reorganization of supply chains (friend shoring, etc.)
- Massive investment / industrial policies (advanced technologies, critical sectors, e.g., IRA, CHIPS Act, Made in China 2025)
- Intervention Priorities
- Boost the competitiveness and growth of Quebec businesses
- Accelerate the green transition of businesses (since 2022)
- Promote community vitality
- Foster the economic resilience of businesses and the regions (temporary)
Delays in Innovation and Techology Adoption
- Issues
- Low productivity vs Canada (-13%) and the U.S. (-57%), and disparities in growth (Canada < U.S.)
- Digitization of the economy and competition to develop and adopt emerging technologies
- Intervention Priorities
- Boost the competitiveness and growth of Quebec businesses
- Accelerate the green transition of businesses (since 2022)
- Promote community vitality
- Foster the economic resilience of businesses and the regions (temporary)
Adapting to Climate Change
- Issues
- Environmental requirements (governments, major contractors, consumers)
- Climate change disruption (disasters, etc.) and the need to adapt
- Intervention Priorities
- Boost the competitiveness and growth of Quebec businesses
- Accelerate the green transition of businesses (since 2022)
- Promote community vitality
- Foster the economic resilience of businesses and the regions (temporary)
Challenges for Devitalized Communities
- Issues
- Increased barriers: demographics, remoteness, infrastructure costs, connectivity, etc.
- Challenge of modernizing so-called “traditional” sectors, each region having a particular industrial structure
- Intervention Priorities
- Accelerate the green transition of businesses (since 2022)
- Promote community vitality
- Foster the economic resilience of businesses and the regions (temporary)
Taking into account the sectors that structure regional economies...
The importance of SMEs in Quebec, all sectors combined*
- More than 275,000 SMEs in Quebec, 72% of which have fewer than 10 employees
- SMEs account for 87% of private sector jobs in the province
CED prioritizes manufacturing sectors and high value-added services
- CED sees sectors as vectors of long-term structuring growth in a given region
*Source: Statistics Canada, Business Register 2022-IV and Industry Canada, Key Small Business Statistics (2022)
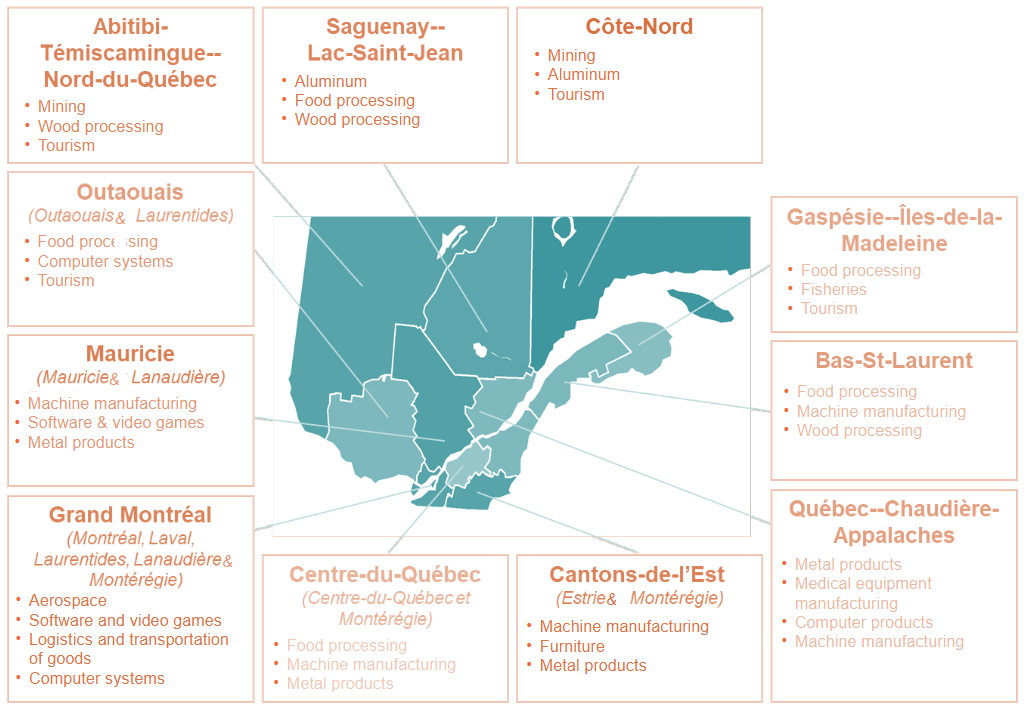
Text version:
- Abitibi-Témiscamingue Nord-du-Québec
- Mining
- Wood processing
- Tourism
- Saguenay - Lac-Saint-Jean
- Aluminum
- Food processing
- Wood processing
- Côte-Nord
- Mining
- Aluminum
- Tourism
- Gaspésie - Îles-de-la-Madeleine
- Food processing
- Fisheries
- Tourism
- Bas-St-Laurent
- Food processing
- Machine manufacturing
- Wood processing
- Québec - Chaudière-Appalaches
- Metal products
- Medical equipment manufacturing
- Computer products
- Machine manufacturing
- Cantons-de-l’Est (Estrie and Montérégie)
- Machine manufacturing
- Furniture
- Metal products
- Centre-du-Québec (Centre-du-Québec and Montérégie)
- Food processing
- Machine manufacturing
- Metal products
- Grand Montréal (Montréal, Laval, Laurentides, Lanaudière and Montérégie)
- Aerospace
- Software and video games
- Logistics and transportation of goods
- Computer systems
- Mauricie (Mauricie and Lanaudière)
- Machine manufacturing
- Software and video games
- Metal products
- Outaouais (Outaouais and Laurentides)
- Food processing
- Computer systems
- Tourism
With growing support for the acceleration of the green transition
Investment
- Green investment target doubled to $50M per year by 2025–2026
- Easing of conditions for SMEs going ahead with their projects
Environmental grid
- Inventory of clients’ green practices and green elements of projects included in new applications for funding under CED programs
Support
- Shoring up of ecosystem support to help SMEs go ahead with their projects
Consultation
- Minister's advisory committee on the green transition
Means of Action (Programs and Initiatives)
Our grant and contribution programs...
Regional Innovation
Support the growth, productivity and competitiveness of SMEs through innovation, and through the development of an innovative regional entrepreneurial environment
- Regional Economic Growth through Innovation (REGI)
Community Vitality
Promote the growth of regions and communities by strengthening their entrepreneurial and industrial fabric through economic diversification; the enhancement of their assets, including tourism; the promotion of foreign investment; and support for economic participation
- Quebec Economic Development Program (QEDP)
- Community Futures Program (CFP)
- Economic Development Initiative – Official Languages (EDI-OL)
Temporary and Targeted Support
Develop and implement temporary initiatives to meet specific needs, with dedicated funding
- National initiatives
- Related to national issues (e.g., Support for regional quantum innovation; Hurricane Fiona Recovery Fund)
- Related to the post-COVID recovery (e.g., Tourism Relief Fund; Jobs and Growth Fund; Aerospace Regional Recovery Initiative; Canada Community Revitalization Fund; Major Festivals and Events Support Initiative)
- Initiatives specific to Quebec (e.g., Assistance for the economic recovery of Lac-Mégantic)
Provide direct and indirect support to SMEs at all stages of their development...
| CED Support | Business Startups | Innovation | Productivity Enhancement |
Commercialization / Market Access |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Projects: | ||||
|
Regional Innovation:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
|
Community Vitality:
|
||||
| Support for SMEs | ||||
|
Regional Innovation:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
|
Community Vitality:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Examples of activities funded:
|
Using our investment approach
Sharing of financial risks / leveraging efforts
SMEs
- Interest-free repayable contributions, generally without guarantee
- Repayment moratorium generally two years
- Repayment generally spread out over five years after the moratorium
NPOs
- Non-repayable contributions
Business-focussed interventions aimed at generating regional benefits
| Age | 9.2 |
|---|---|
| Number of Employees | 20 |
| Sales Revenue | $2.7M |
| Main Area of Activity | Manufacturing |
*The median provides a picture of our typical SME clientele. CED does, however, support SMEs of all sizes, and the amount of funding awarded depends on the nature of the project.
Types of NPOs Funded (non-exhaustive)
- Industrial clusters
- Incubators/accelerators
- Technology transfer centres
- Promoting and structuring tourist attractions
- Attracting direct foreign investment
- Community Futures Development Corporations (CFDCs) / Business Development Centres (BDCs) (in rural areas)
That results in good projects
- Regional Innovation
- Innovation and Technology Transfer: $3.04M in funding for Cintech agroalimentaire, a college centre for technology transfer, for the acquisition and installation of equipment for developing new sources of foods rich in plant-based proteins.
- Productivity, Digitization and Expansion: $1.2M in funding for LOOP Mission, a young circular economy SME headed-up and co-founded by a woman entrepreneur. CED’s assistance will serve to purchase digital equipment to enhance the company’s production capacity and productivity.
- Commercialization and Exports: $200,000 in funding for Interloom Inc., a Gatineau-based business that specializes in the design of object-oriented management tools. The assistance will allow the business to market an innovative software solution.
- Regional Innovation Ecosystems: $1.4M in funding for the Centre québécois d’innovation en biotechnologie (CQIB), an incubator that facilitates the creation and growth of life sciences / medical technology SMEs. The assistance will be used for the organization’s operations.
- Community Vitality
- Promotion of Assets and the Regions: $985,000 in funding for the Société récréo-touristique de Desbiens, the NPO that manages the La Caverne du Trou de la Fée (Métabetchouan River) tourism site. The funding will serve to add aerial walkways to make the site more attractive.
- Local Development: $1.13M for microbrewery À l'abri de la tempête for expansion work and the purchase of wastewater production and treatment equipment to support the growth of the business and the enhancement of its productivity.
- Temporary and Targeted Support
- Economic recovery Quebec: $532K in funding for the Town of Lac-Mégantic to support its ecological transition through the construction of a public space with a multifunctional solar shelter that will showcase renewable energy production, storage and control technologies.
- Post-Covid Measure: $7.27M in funding for Air Inuit Ltd. to improve service for Nunavik’s coastal villages through the acquisition of upgraded computer, aircraft maintenance and baggage handling equipment.
That produce results and tangible benefits
In 2022–2023
- Regular programs: $223M invested to support 699 projects
- Temporary targeted initiatives: $269M invested to support 626 projects

Text version:
| Invested by CED | Invested by Other Sources | Grant and Contribution Program |
|---|---|---|
| $1 | $4.38 | Regional Innovation |
| $1 | $2.91 | Community Vitality |
| $1 | $2.25 | Targeted Support |
Over the past seven years* (on average)
CED has invested $230M annually in its regular programs:
- $148M / year to support regional innovation
- $82M / year to support community vitality
* Data based on projects with expenditures. Subject to change.
Our budgets: expenditure profile and trends
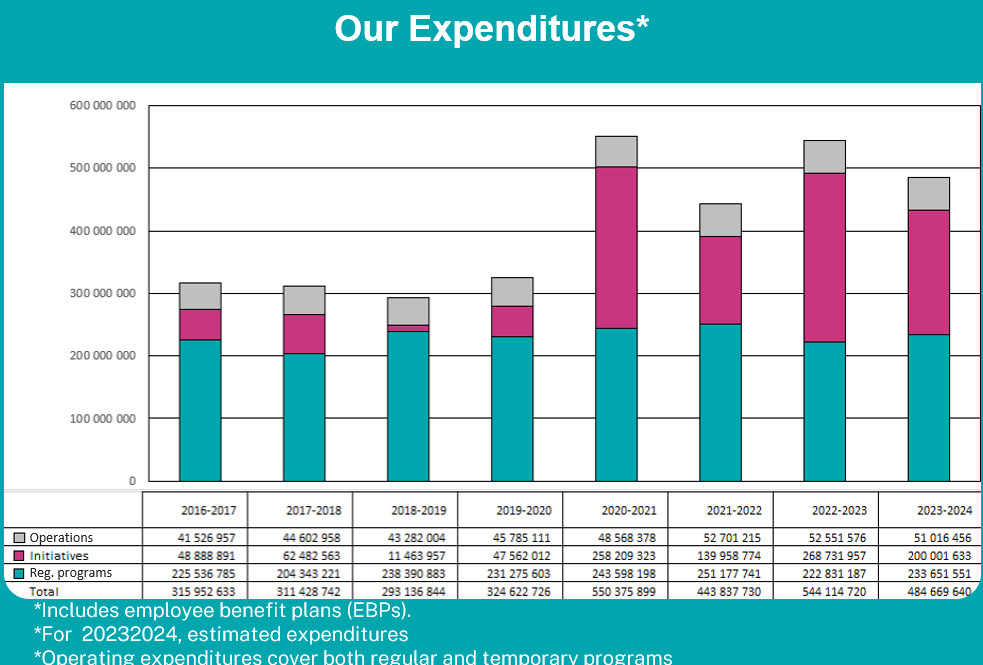
Text version:
| 2016-2017 | 2017-2018 | 2018-2019 | 2019-2020 | 2020-2021 | 2021-2022 | 2022-2023 | 2023-2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operations | 41 526 957 | 44 602 958 | 43 282 004 | 45 785 111 | 48 568 378 | 52 701 215 | 52 551 576 | 51 016 456 |
| Initiatives | 48 888 891 | 62 482 563 | 11 463 957 | 47 562 012 | 258 209 323 | 139 958 774 | 268 731 957 | 200 001 633 |
| Reg. programs | 225 536 785 | 204 343 221 | 238 390 883 | 231 275 603 | 243 598 198 | 251 177 741 | 222 831 187 | 233 651 551 |
| Total | 315 952 633 | 311 428 742 | 293 136 844 | 324 622 726 | 550 375 899 | 443 837 730 | 544 114 720 | 484 669 640 |
* Includes employee benefit plans (EBPs).
* For 2023-2024, estimated expenditures
* Operating expenditures cover both regular and temporary programs
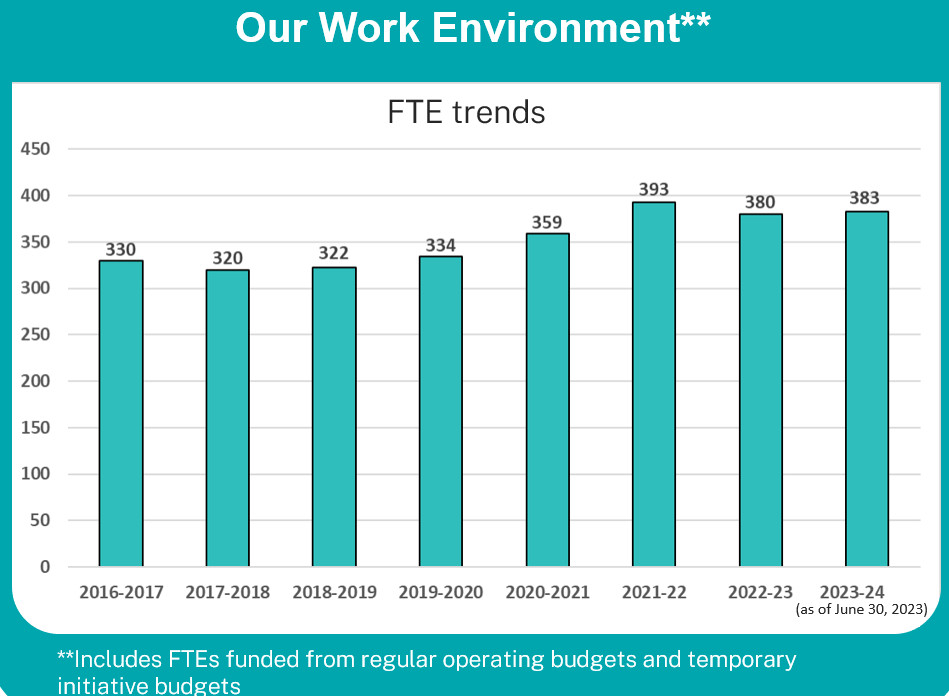
Text version:
| 2016-2017 | 2017-2018 | 2018-2019 | 2019-2020 | 2020-2021 | 2021-2022 | 2022-2023 | 2023-2024 (as of June 30, 2023) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTE trends | 330 | 320 | 322 | 334 | 359 | 393 | 380 | 383 |
**Includes FTEs funded from regular operating budgets and temporary initiative budgets
Organizational structure
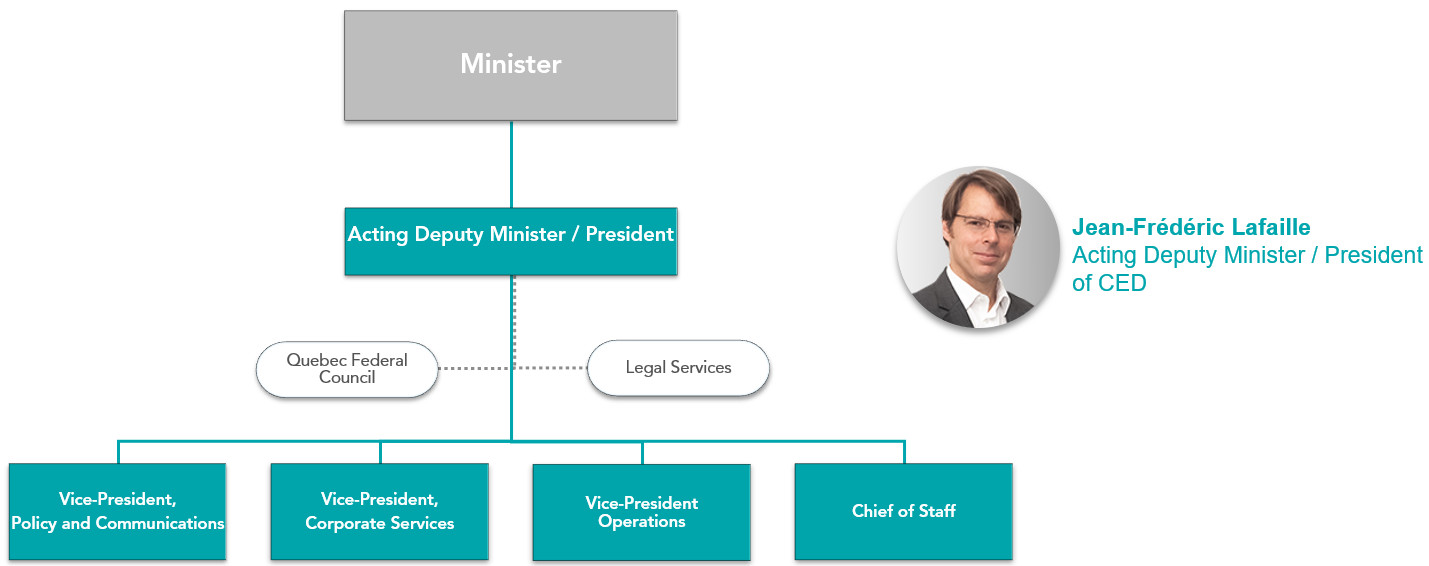
Text version:
- Minister
- Acting Deputy Minister / President of CED (Jean-Frédéric Lafaille)
- Quebec Federal Council
- Vice-President Policy and Communications
- Vice-President Corporate Services
- Vice-President Operations
- Chief of Staff
- Legal Services
- Vice-President Policy and Communications
- Vice-President Corporate Services
- Vice-President Operations
- Chief of Staff
- Quebec Federal Council
- Acting Deputy Minister / President of CED (Jean-Frédéric Lafaille)
Being asked questions?
Useful key messages about CED
- Canada Economic Development for Quebec Regions is the key federal partner in regional economic development in Quebec.
- Through its 12 community-focused business offices located across Quebec, CED assists businesses and the regions with a view to boosting the prosperity of our economy and our communities by supporting projects that generate long-term economic benefits.
- CED acts as an accelerator of economic growth: its interventions support regional innovation, the growth of SMEs, the vitality of Quebec communities, and the long-term competitiveness of our economy, specifically by helping accelerate its environmental transition.
- CED also plays a key integration and networking role to help bring together the right partners around a given project.
- CED maintains close collaborative relations with its federal partners and the Government of Quebec and aims for complementarity of approaches.
Your welcome
Support you, for a fluid and swift transition
- Find out your needs and offer you our support
- Put in place the necessary processes so that you are up and running as quickly as possible
Identify your orientations
- Discuss your intervention priorities and provide you with our best advice
- Present and discuss our current initiatives and programs